Main principle concept
Introduction
This chapter will introduce the main principles of ByConity and it's query execution. ByConity's query execution process is shown in the figure below. First, ByConity will obtain the Metadata information required for the query through the Metadata service. Then ByConity will generate an efficient query plan through the optimizer according to the user's SQL, and schedule it to the corresponding calculation group to read the data and execute it. Finally, the result set is summarized and sent back to the Client.
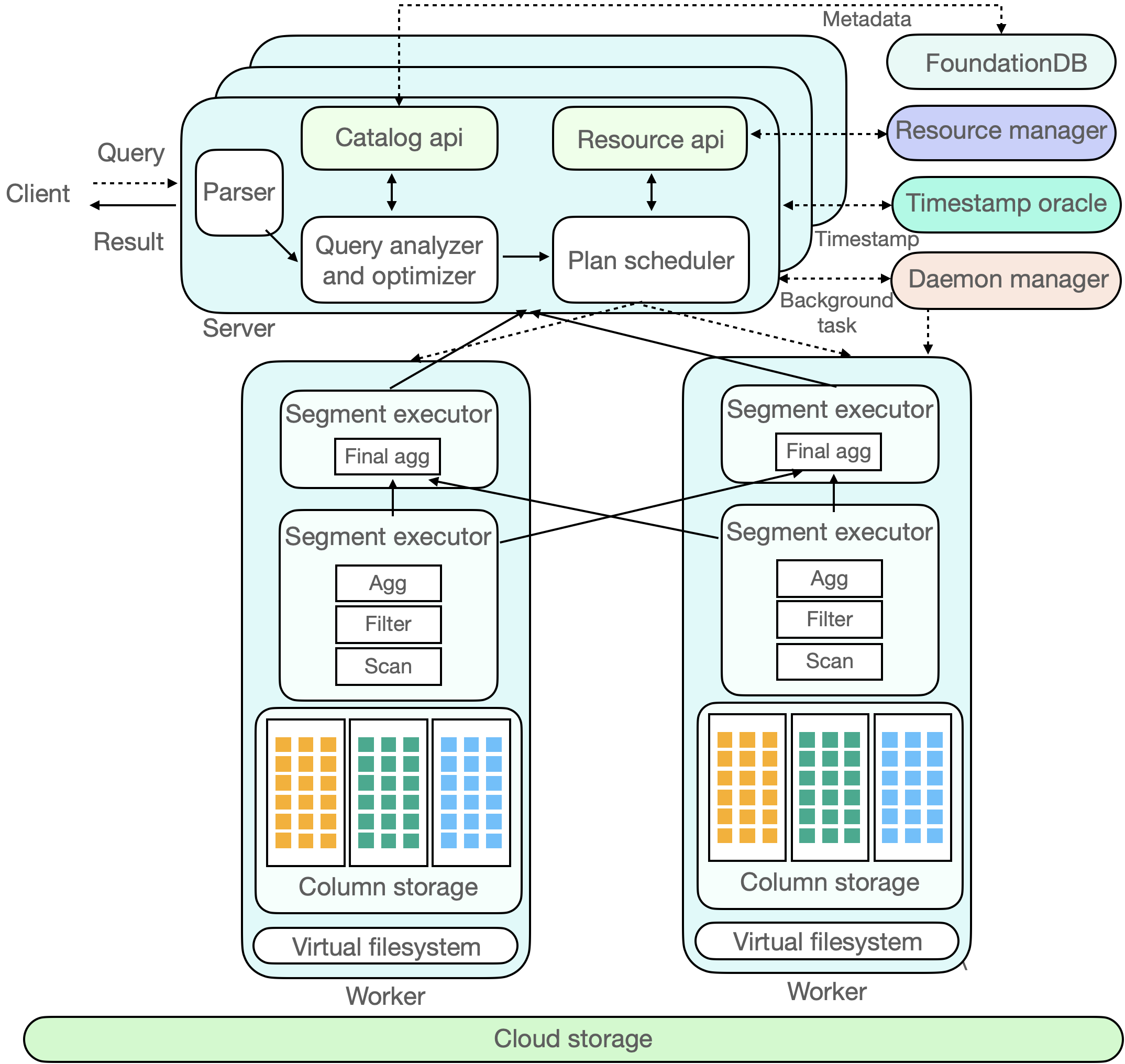
Metadata Management(Catalog Service)
The function of Metadata Management (Catalog Service) is mainly to read and write the Metadata of read and write requests. Metadata service is a very critical service, which determines the availability and correctness of queries. Not only does ByConity provide highly available and scalable Metadata management services, but it also implements complete transaction semantics guarantee (ACID) on top of it. In addition, ByConity also uses caching to provide low-delay reading of the raw data involved in queries to ensure efficient and stable query performance.
Query Optimizer
The Query Optimizer is one of the cores of the Database System. An excellent optimizer can greatly improve query performance. Especially in complex query scenarios, the optimizer can bring performance improvements of several to hundreds times.
ByConity's self-developed optimizer provides extreme optimization capabilities based on four major optimization directions:
- RBO: rule-based optimization capabilities. Support: column clipping, partition clipping, expression simplification, subquery disassociation, predicate push-down, redundant operator elimination, outer-JOIN to INNER-JOIN, operator push-down storage, distributed operator splitting and other common heuristic optimization capabilities.
- CBO : Cost-based optimization capabilities. Support: Join Reorder, Outer-Join Reorder, Join/Agg Reorder, CTE, Materialized View, Dynamic Filter Push-Down, Magic Set and other cost-based optimization capabilities. And integrates Property Enforcement for distributed plans.
- DBO: Optimization capabilities based on data dependencies. Support: unique key, functional dependency, Order dependency, Inclusion dependency and other optimization capabilities based on data dependencies.
- HBO: Optimization ability based on query feedback. Support: dynamic adjustment of cardinality estimation, dynamic adjustment of parallelism, dynamic adjustment of Operating Plan and other optimization capabilities based on historical execution feedback.
Virtual Warehouse
Virtual Warehouse (VW for short) is a virtual organization of computing resources. Computing resources can be divided into multiple virtual clusters on demand to provide physical resource isolation between different tenants. Each virtual cluster contains 0 to more computing nodes, and performs dynamic volume expansion and contraction according to actual resource requirements.
There are two ways to calculate volume expansion and contraction:
- One is vertical expansion, that is, adjusting the number of CPU cores and memory size of the computing group.
- The other is horizontal expansion, increase or decrease the number of computing groups, improve system concurrency.
In the architecture of storage-computing separation, computing resources and storage resources are decoupled and stateless. The volume expansion and contraction process does not need to migrate and balance data. This enables fast elastic volume expansion and contraction can be achieved.
Computing nodes are mainly responsible for computing tasks, which can be data writing, user queries, or some background tasks. Under the storage-computing separation architecture of ByConity, user queries can realize read and write separation to reduce mutual interference between read and write jobs. User queries and background tasks can share the same computing node to improve utilization, or independent computing nodes can be used to ensure strict resource isolation. Users can build multiple computing groups according to the characteristics, priorities and business categories of computing tasks, and set different resource elasticity strategies to improve computing efficiency and reduce costs.
Virtual File System (VFS)
ByConity uses cloud storage services such as HDFS or S3 as the data storage layer to store actual data, indexes, etc. The data files of the data table are stored in the remote unified distributed storage system, which is separated from the computing nodes. The underlying storage system may correspond to different types of distributed systems. Such as HDFS, Amazon S3, Google cloud storage, Azure blob storage, Alibaba Cloud object storage , etc.
Different distributed storage systems have many different functions and different performance, which will affect the design and implementation of functions. For example, HDFS does not support file update; S3 object move operation requires reoperation to copy data, etc. ByConity provides a unified abstract file system interface to the computing layer through the service of storage. The storage layer adopts S3 or HDFS to be transparent to the computing layer; the computing layer can support ByConity's own computing engine, and can easily connect to other computing engines in the future, such as Presto, Spark, etc.
Columnar Storage
Similar to mainstream analytical data, ByConity adopts a columnar storage format to reduce unnecessary data IO to improve query performance, and efficiently compress data to reduce storage costs. In addition, for continuously stored columnar data, ByConity further improves query performance through vectorized execution technology.
Main process
Query execution
- Users submit Select Query to the service node.
- Obtain the required Metadata information from the Metadata service, perform Parsing, Planning, Optimising on Query, and generate Operating Plan.
- The service node schedules the Operating Plan according to the available computing resources and sends tasks to the computing node.
- The computing node receives the Query subquery.
- Query obtains data from the virtual file system (VFS), executes it on the computing node according to the Query's Operating Plan, and sends back the calculation results to the service node for summary.
Data write
- The user submits a Write Query to the service node.
- The service node selects the appropriate write node to execute the write request according to the scheduling policy.
- The write node performs the write, writes the data to the local disk and dumps it to the cloud storage side.
- Submit part Metadata to the Catalog Service, submit the transaction, and the write is completed.
Calculate group volume expansion and contraction
The Resource Manager is responsible for unified management and scheduling of computing resources. It can collect performance data and resource usage of each computing group, dynamically allocate resources for read and write tasks and background tasks, and perform volume expansion and contraction to improve resources. The components of ByConity have been containerized, and it is very convenient to perform volume expansion and contraction on the specified computing group by adjusting the number of replicas of kubernets. In addition, dynamic volume expansion and contraction can be achieved by setting the volume expansion and contraction threshold of kubernets in combination with calculating group resource usage.